The pineal gland, also known as the “third eye,” is a small endocrine gland located deep in the brain. Despite its relatively small size, the pineal gland plays a crucial role in regulating several important bodily functions, including sleep, mood, and reproductive health. In this blog post, we will explore the pineal gland in greater detail, including its anatomy, functions, and potential health benefits.
Anatomy of the Pineal Gland:
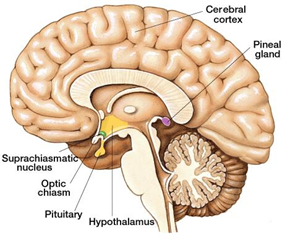
The pineal gland is located in the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres. It is a small, pinecone-shaped gland that measures around 5-8mm in length and 2-4mm in width. The gland is composed of specialized cells called pinealocytes, which are responsible for producing and secreting the hormone melatonin. In addition to pinealocytes, the gland also contains other types of cells, including astrocytes and neurons.
Functions of the Pineal Gland:
The primary function of the pineal gland is to regulate the body’s circadian rhythm, or internal clock. The gland is responsible for producing and releasing the hormone melatonin, which is involved in regulating sleep patterns. Melatonin production is stimulated by darkness and inhibited by light, which is why people tend to feel more awake during the daytime and more sleepy at night.
In addition to regulating sleep patterns, the pineal gland is also thought to play a role in mood regulation. Studies have shown that melatonin levels are lower in people with depression, and that melatonin supplementation may improve symptoms of depression and anxiety.
The pineal gland is also involved in regulating reproductive health. It produces and releases a hormone called gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which stimulates the release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the pituitary gland. These hormones play a crucial role in regulating menstrual cycles in women and testosterone production in men.
Potential Health Benefits of the Pineal Gland:
While more research is needed, some studies suggest that the pineal gland may offer several potential health benefits. For example, research has shown that melatonin may have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, which could help protect against certain chronic diseases. Melatonin has also been shown to improve sleep quality, which could have a positive impact on overall health and well-being.
Some alternative medicine practitioners believe that the pineal gland is capable of producing other hormones and neurotransmitters that have a wide range of health benefits. However, there is currently no scientific evidence to support these claims.
In conclusion, the pineal gland is a small but important gland that plays a crucial role in regulating several key bodily functions. Its primary function is to regulate the body’s circadian rhythm, but it is also involved in mood regulation and reproductive health. While more research is needed to fully understand the potential health benefits of the pineal gland, existing research suggests that it may offer several promising therapeutic benefits.

